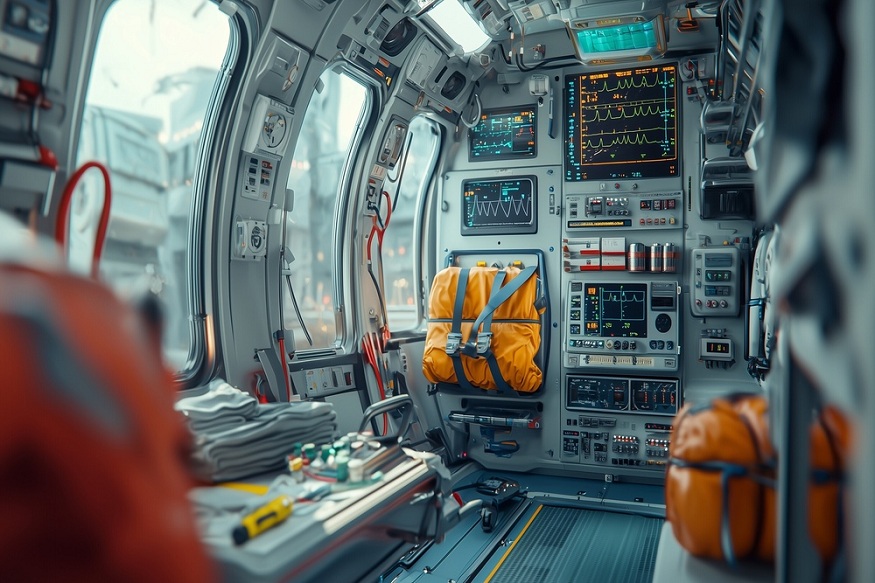
Beyond the Stretcher: Advanced Devices Used in Air Medical Response
Many believe that air medical helicopters transport only stretchers and essential first aid gear. The truth is much more astonishing. These airborne medical centers incorporate remarkable technology into areas smaller than typical walk-in closets. Every device has a distinct function: sustaining patients’ lives while en route to the hospital.
Portable Heart Machines
Cardiac emergencies and heart attacks occur often during medical flights. Teams transport portable defibrillators capable of reviving a halted heart with electric shocks. These devices automatically evaluate heart rhythms and instruct medical teams on the precise actions to take. Contemporary defibrillators function as sophisticated heart monitors as well. They monitor the heart’s electrical activity and present the data on clear displays. Certain models can also regulate the heart if it beats too slowly, functioning as a temporary electronic heartbeat. The batteries in these gadgets endure for hours, which is vital during extended flights to remote hospitals. They also withstand vibrations and abrupt movements that could harm standard hospital equipment.
Blood Analysis in Flight
Small lab instruments now accompany medical helicopters. These analyzers provide blood test results quickly. Vital signs can be monitored before arriving at the hospital. This data assists medical teams in making improved treatment choices while in flight. If a person experiences critically low blood sugar, teams can administer glucose right away rather than speculating about the issue.
Breathing Support Systems
Ventilators assist patients in breathing when their lungs are not functioning correctly. The people at LifePort explain that the LifePort MEDEVAC equipment comprises specialized ventilators intended for aircraft. These devices adjust to altitude changes.
Flight ventilators consume less oxygen compared to hospital models. Given that helicopters hold restricted oxygen reserves, efficiency is crucially important. Certain models can alternate between various breathing modes based on the specific requirements of each patient. Transport ventilators are significantly more compact than standard hospital machines. They need to fit snugly in confined areas while still delivering the same level of care that patients would obtain in intensive care units.
Temperature Control Technology
Maintaining the proper temperature for patients during flights necessitates specialized equipment. Heating blankets connected to the aircraft’s electrical system protect trauma patients from hypothermia. These blankets spread warmth uniformly and won’t become too hot even on extended flights. Certain helicopters are equipped with cooling systems for individuals suffering from heatstroke or elevated temperatures. These systems function like individual air conditioners, distributing cool air throughout the patient’s body.
Medication Delivery Systems
IV pumps regulate the speed at which patients get medications and fluids. Aircraft models withstand shocks and vibrations that would impact standard pumps. They operate on battery power and employ unique safety systems to avoid hazardous movements while in the air. Intelligent pumps can determine medication doses according to patient weight and health conditions. They also notify crews if someone attempts to provide excessive or insufficient medication. These safety mechanisms avert hazardous errors in critical emergency circumstances.
Advanced Communication Tools
Medical teams must communicate with hospitals during flights. Digital communication systems transmit patient data, such as heart rhythms and vital signs, straight to emergency departments. Doctors can analyze this information and create treatment strategies prior to helicopter arrivals. Some systems have video features that enable ground-based experts to observe patients and direct treatment choices. A cardiologist could monitor a heart attack patient’s status live and counsel the flight crew.
Conclusion
Air medical response has advanced significantly beyond basic stretcher transportation. Current helicopters are equipped with technology that competes with many hospital emergency departments. All devices aim for the same objective: providing patients with the greatest likelihood of survival. These improvements enable quick access to medical care. Helicopters become airborne ICUs, thanks to expert teams and technology.